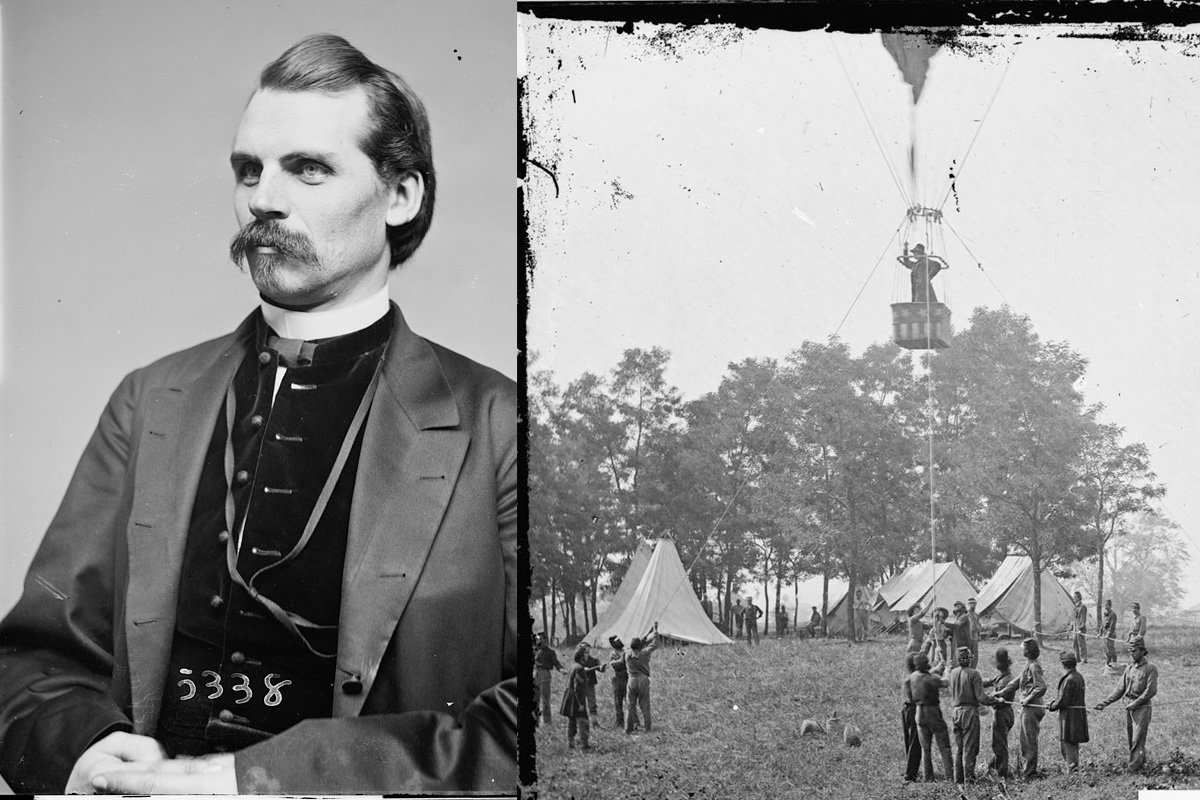
Thaddeus Lowe, left, helped make President Abraham Lincoln’s air force a reality. He is seen here, right, observing a battle from his balloon, called Intrepid, during the Peninsula campaign in 1862. Photos courtesy of the Library of Congress. Composite by Coffee or Die Magazine.
During the early weeks of the Civil War, accomplished aeronaut Thaddeus S.C. Lowe approached President Abraham Lincoln with a maverick idea. He proposed outfitting the US military with hydrogen balloons to conduct aerial reconnaissance on the battlefield. This warfare tactic predated airplanes and had zero operational application at any prior point in American history. The idea evolved into what became known as “Lincoln’s Air Force,” a fleet of balloonists who leveraged their bird’s-eye view to conduct military surveillance operations against Confederate troops during the Civil War.
But first, Lowe had to convince Lincoln the idea had value.
“The war department gave the Smithsonian $250 to fund a demonstration balloon flight,” said Tom Crouch, senior curator in the National Air and Space Museum’s Aeronautics Division, in a 2011 video.
Lowe demonstrated the strategic potential of his idea on June 18, 1861, when he took flight from the grounds of the National Mall in Washington, DC. The balloon, named Enterprise, remained tethered to the ground to ensure the demonstration could be properly observed. Lowe and two other men, a telegrapher and the owner of a telegraph company, floated up into the air. From 500 feet above the ground, Lowe successfully sent the world’s first airborne telegram to Lincoln at the White House.

Impressed by the demonstration — and with news spreading of the emergence of aerial photography after Boston photographer James Wallace Black became the first person in the US to capture and produce an aerial photograph — Lincoln greenlighted the creation of the Union Army Balloon Corps and named Lowe chief aeronaut.
John LaMountain, another civilian aeronaut, joined the balloon corps ranks and conducted the first untethered aerial surveillance flight in the US when he spied on a Confederate camp in Virginia.
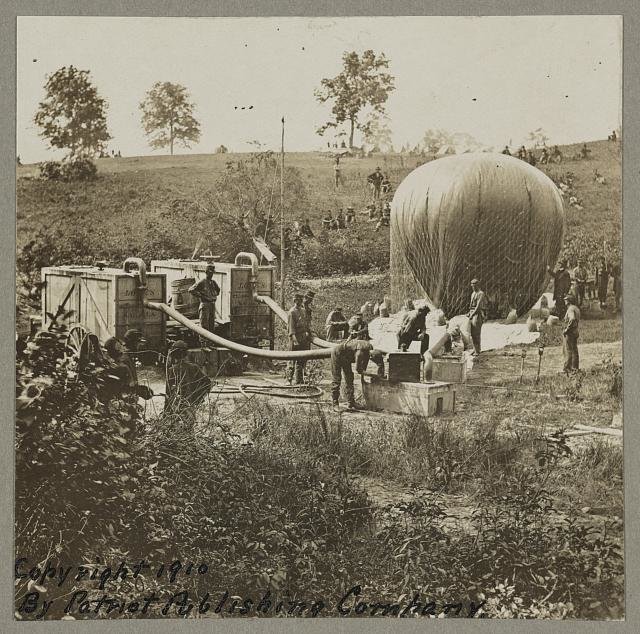
The corps boasted a fleet of seven balloons: Union, Intrepid, Constitution, United States, Washington, Eagle, and Excelsior. Each differed in size. The Union and Intrepid were the largest and could carry five people in their baskets, while the comparatively diminutive Eagle and Excelsior could hold just one person.
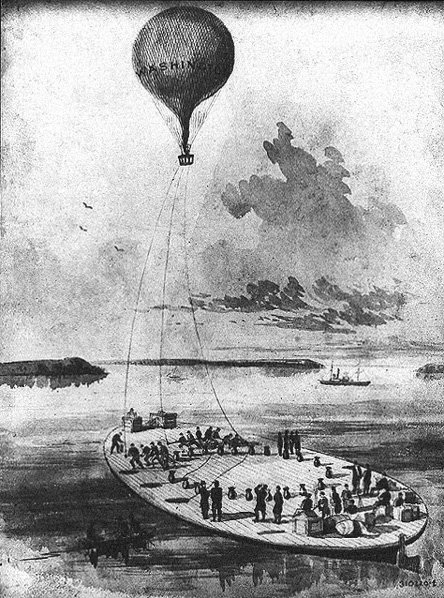
The balloonists were tethered along the Potomac River and provided surveillance to protect the capital from Confederate attacks. The operators could reach elevations of 1,000 feet and commonly used flags as signals and a telegraph to deliver messages to officers and soldiers on the ground.
“The balloons were purposely colorful and easily visible to intimidate Confederate troops, making them feel as if nearby Union troops were watching them,” writes Hannah Chan in an article published by the Federal Aviation Administration. “There were a few instances where intelligence was gathered from a free flight, but only experts, like LaMountain, were capable of doing so.”
In August 1861, Lowe converted an old coal barge into a balloon barge, a de facto aircraft carrier, named the USS George Washington Parke Custis. Soon thereafter, he successfully launched a balloon from the vessel, combining airborne and naval forces for the first time in US military history. LaMountain also pulled off tricky naval liftoffs, but used a steamer and a tugboat rather than a barge.
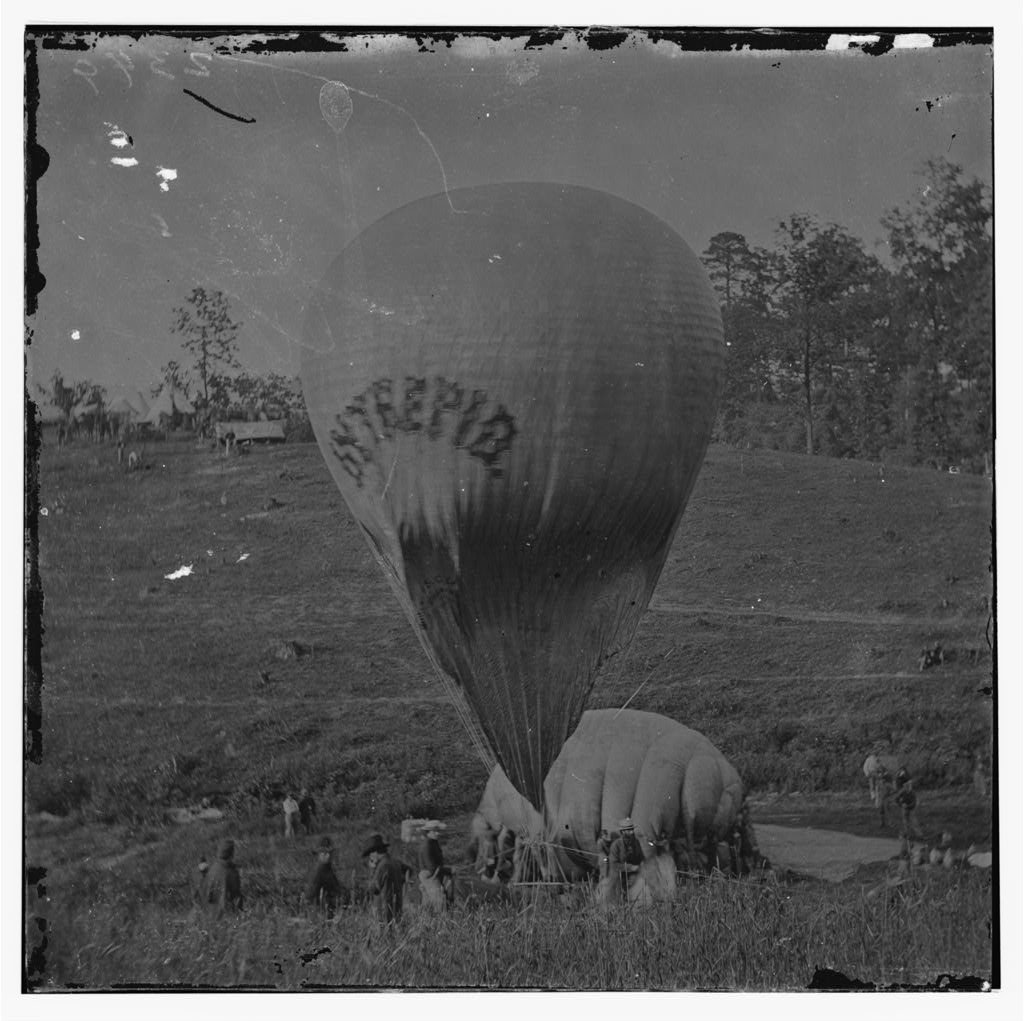

The Union Army Balloon Corps provided artillery troops with intelligence to accurately fire upon Confederate positions stationed at Falls Church, Virginia, despite not having a visual on their targets. These balloonists also assisted in the Battle of Island Number Ten, the Peninsula campaign, the Battle of Fair Oaks, the sieges of Yorktown and Fredericksburg, and several other battles.
Confederate troops routinely shot at the balloonists during the Peninsula campaign, but the balloons survived. The Confederacy also tried to trick the spying balloonists and conceal their troop locations by creating fake camps and artillery emplacements.
The Confederacy created a smaller version of the balloon corps in the spring of 1862, but soon experienced mounting problems. For all their strategic advantages, the reconnaissance balloons were also plagued with communication and logistics issues.
The Union Army Balloon Corps didn’t survive the war and disbanded in 1863. Although its existence was brief, Lincoln’s innovative air force helped change the course of aviation warfare and reconnaissance, paving the way for the modern US Air Force to become a crucial element in military and humanitarian missions around the globe.
Read Next:

Matt Fratus is a history staff writer for Coffee or Die. He prides himself on uncovering the most fascinating tales of history by sharing them through any means of engaging storytelling. He writes for his micro-blog @LateNightHistory on Instagram, where he shares the story behind the image. He is also the host of the Late Night History podcast. When not writing about history, Matt enjoys volunteering for One More Wave and rooting for Boston sports teams.
BRCC and Bad Moon Print Press team up for an exclusive, limited-edition T-shirt design!
BRCC partners with Team Room Design for an exclusive T-shirt release!
Thirty Seconds Out has partnered with BRCC for an exclusive shirt design invoking the God of Winter.
Lucas O'Hara of Grizzly Forge has teamed up with BRCC for a badass, exclusive Shirt Club T-shirt design featuring his most popular knife and tiomahawk.
Coffee or Die sits down with one of the graphic designers behind Black Rifle Coffee's signature look and vibe.
Biden will award the Medal of Honor to a Vietnam War Army helicopter pilot who risked his life to save a reconnaissance team from almost certain death.
Ever wonder how much Jack Mandaville would f*ck sh*t up if he went back in time? The American Revolution didn't even see him coming.
A nearly 200-year-old West Point time capsule that at first appeared to yield little more than dust contains hidden treasure, the US Military Academy said.












